Booking an ultrasound appointment with RDG—whether at your home or one of our medical clinics—is simple, quick, and personalized. We offer several convenient contact methods:
We will contact you with available time slots and relevant instructions. We are committed to providing prompt, courteous, and personalized responses. In most cases, we can offer an appointment within a short time frame based on team availability and your location.
Appointments are adapted to your schedule—including evenings, weekends, and urgent requests. If special preparation is needed (e.g., fasting, drinking water, or specific clothing), you’ll receive clear instructions in advance.
RDG’s ultrasound services offer advanced, accurate, and accessible diagnostic imaging tailored to your individual needs. You can choose to:
In-clinic exams are conducted by an experienced radiologist. A certified technician performs at-home exams. In both cases, the service is pre-scheduled to align with your availability and medical needs.
All ultrasound scans are interpreted by a board-certified radiologist with subspecialty expertise.
Results are delivered promptly, accompanied by professional support, clear explanations, and the opportunity to speak directly with the interpreting radiologist.
Common studies include abdominal, renal, bladder, thyroid, testicular, neck, and limb vein ultrasounds. Follow-up or focused scans can be performed based on physician referral.
Portable devices offer high-resolution imaging that meets the highest clinical standards. The exam is done privately, in a calm and proper environment, with no compromise on quality or professionalism. Flexible scheduling is available, including urgent requests. Each study is interpreted in the full context of the patient’s medical history and clinical background.
At Home:
After scheduling, a certified technician visits your home with mobile equipment. The scan is performed on your bed or another comfortable surface in a respectful and quiet setting. The procedure follows the same clinical standards as in a medical center.
In Clinic:
You will check in briefly before meeting a radiologist who performs the scan using gel and a transducer over the examined area. The procedure is non-invasive, painless, and takes about 10–30 minutes. The radiologist reviews the images in real-time and records findings.
At Home:
After the radiologist reviews the images, the patient receives an SMS and email with a secure link to the report. Access requires a username and password for complete privacy. Reports are written in clear, patient-friendly language.
In Clinic:
The radiologist explains findings during the exam. The final report is sent shortly after via a secure digital file.
Whether you choose to be tested at a clinic or home, RDG is committed to providing accurate results, professional guidance, and a thorough understanding of your scan results.
We believe modern healthcare begins with personal attention—and we combine accessibility, expertise, and cutting-edge technology to serve you wherever you are, without compromise.

A fast and effective method for evaluating the gallbladder and its contents. This exam can detect gallstones, wall thickening, inflammation, or obstruction. It is essential in diagnosing acute or chronic cholecystitis and monitoring suspicious findings. The test is performed after fasting to optimize gallbladder and biliary tract imaging. It is non-invasive, highly accurate, and commonly used for upper abdominal pain assessment.
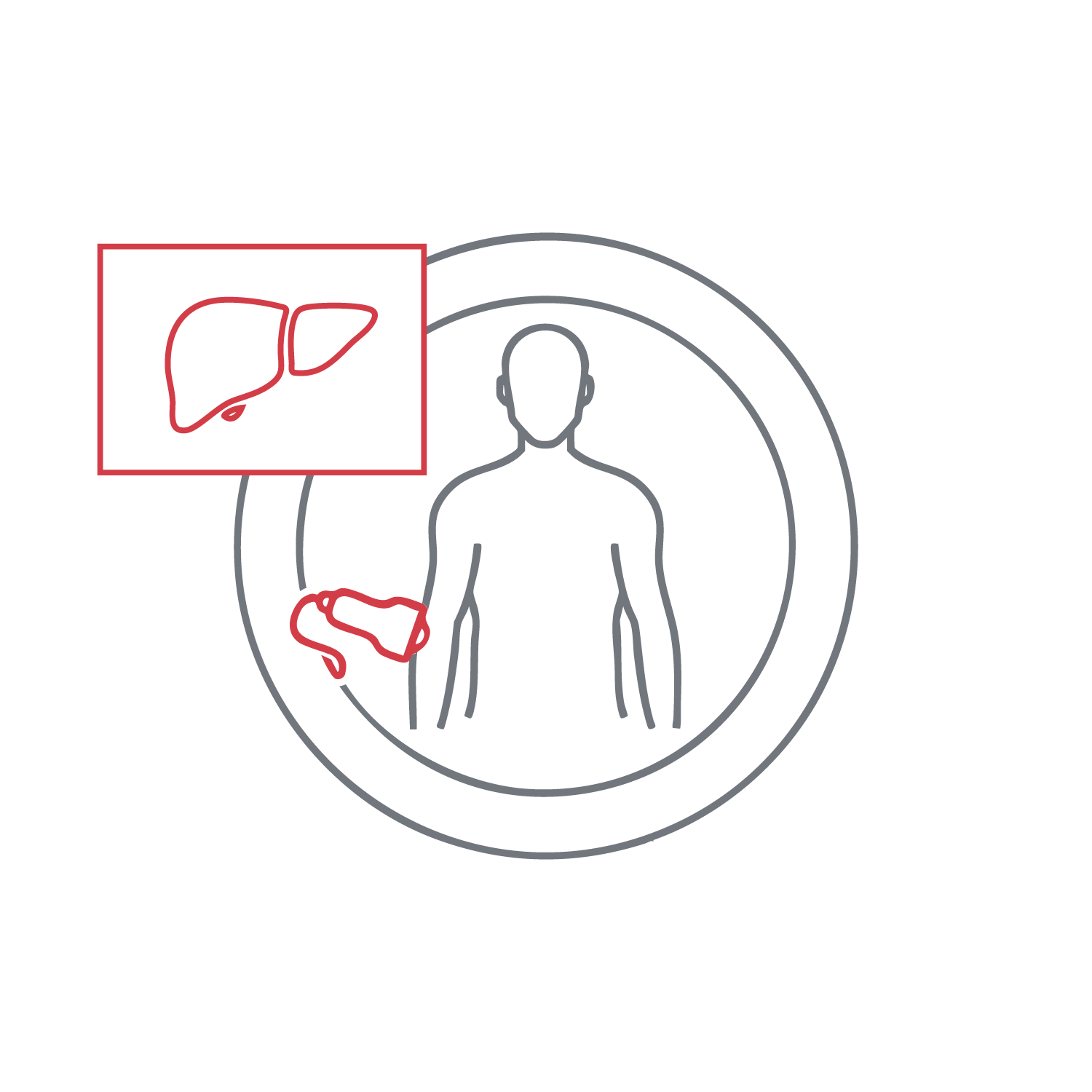

This test evaluates liver texture, size, and anatomical integrity. It detects focal lesions such as tumors, cysts, or hemangiomas, as well as diffuse changes like fatty liver or cirrhosis. Liver ultrasound is important for both initial diagnosis and follow-up. Its high availability and lack of radiation make it a fundamental tool in investigating gastrointestinal symptoms and liver-related conditions.
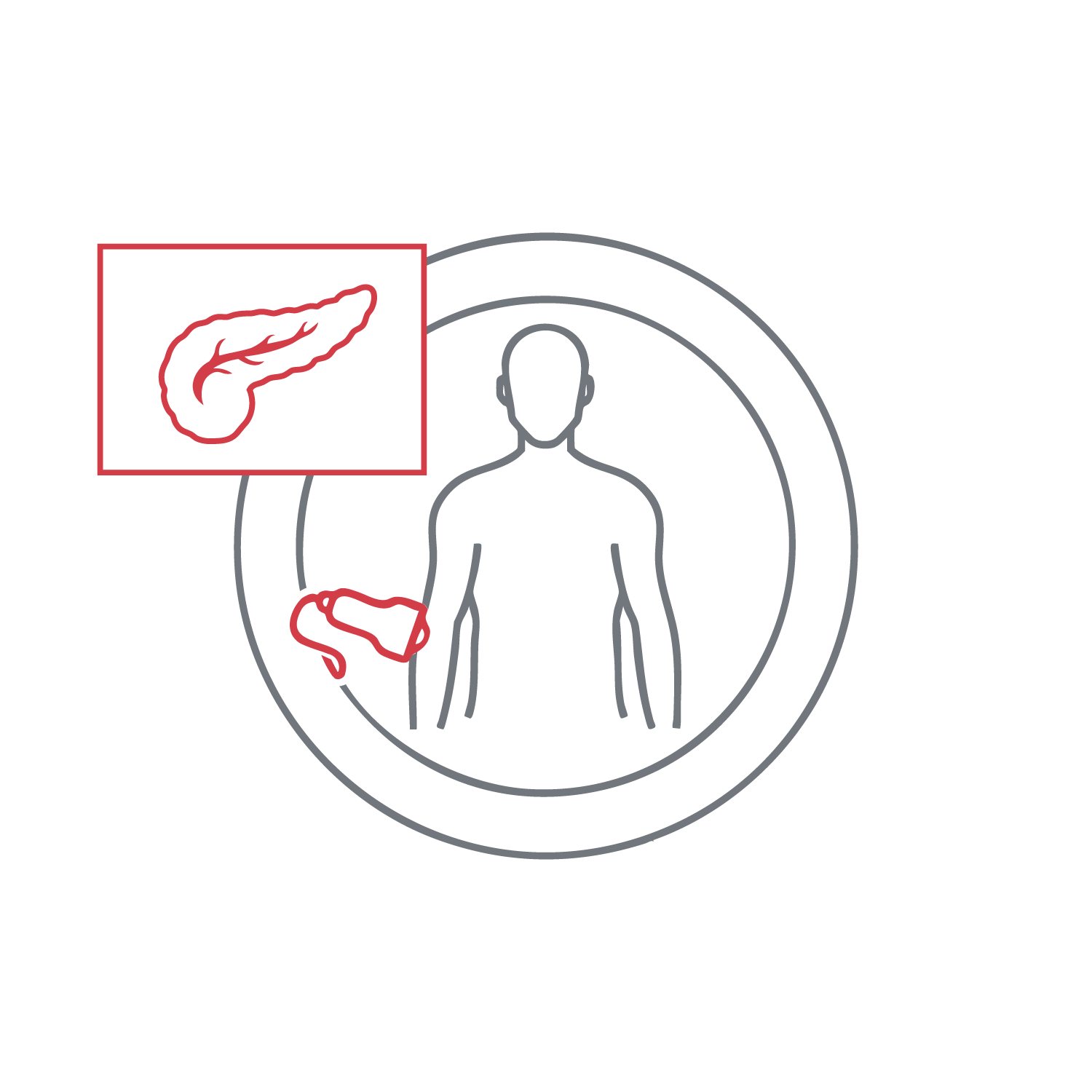

Due to its anatomical location, pancreas imaging can be challenging, but the gland can be visualized clearly in many cases. This scan helps identify masses, cysts, inflammation (e.g., pancreatitis), and changes in tissue texture. Fasting is sometimes required to improve imaging quality. This exam is crucial for evaluating upper abdominal pain and general gastrointestinal symptoms. Accurate interpretation is key for further clinical decision-making.
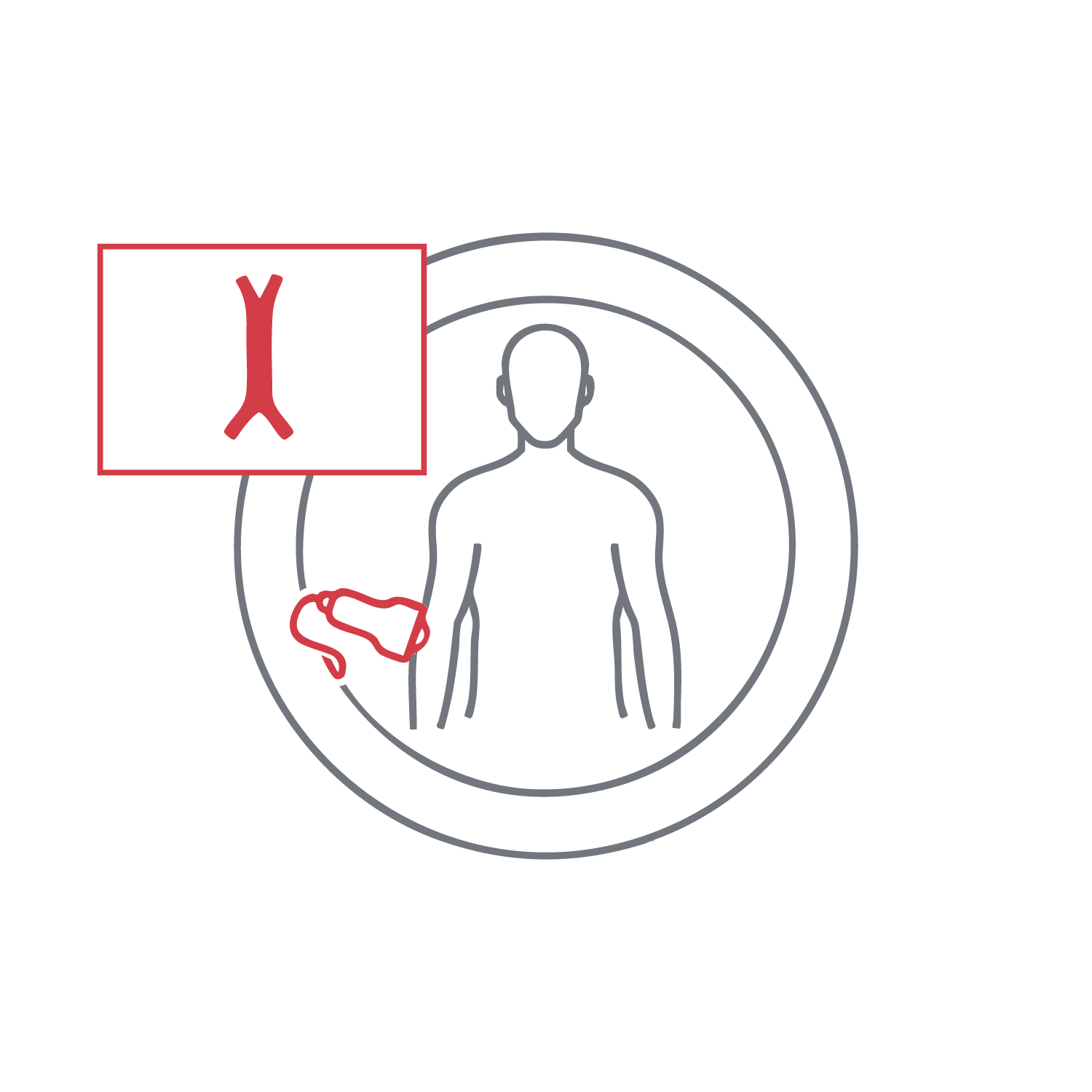

Used to measure aortic diameter and rule out aneurysms. It plays a critical role in the early detection of life-threatening conditions. The scan can identify aortic dilatations or atherosclerosis quickly and non-invasively, both in routine and emergency settings. Its findings significantly impact clinical decisions.
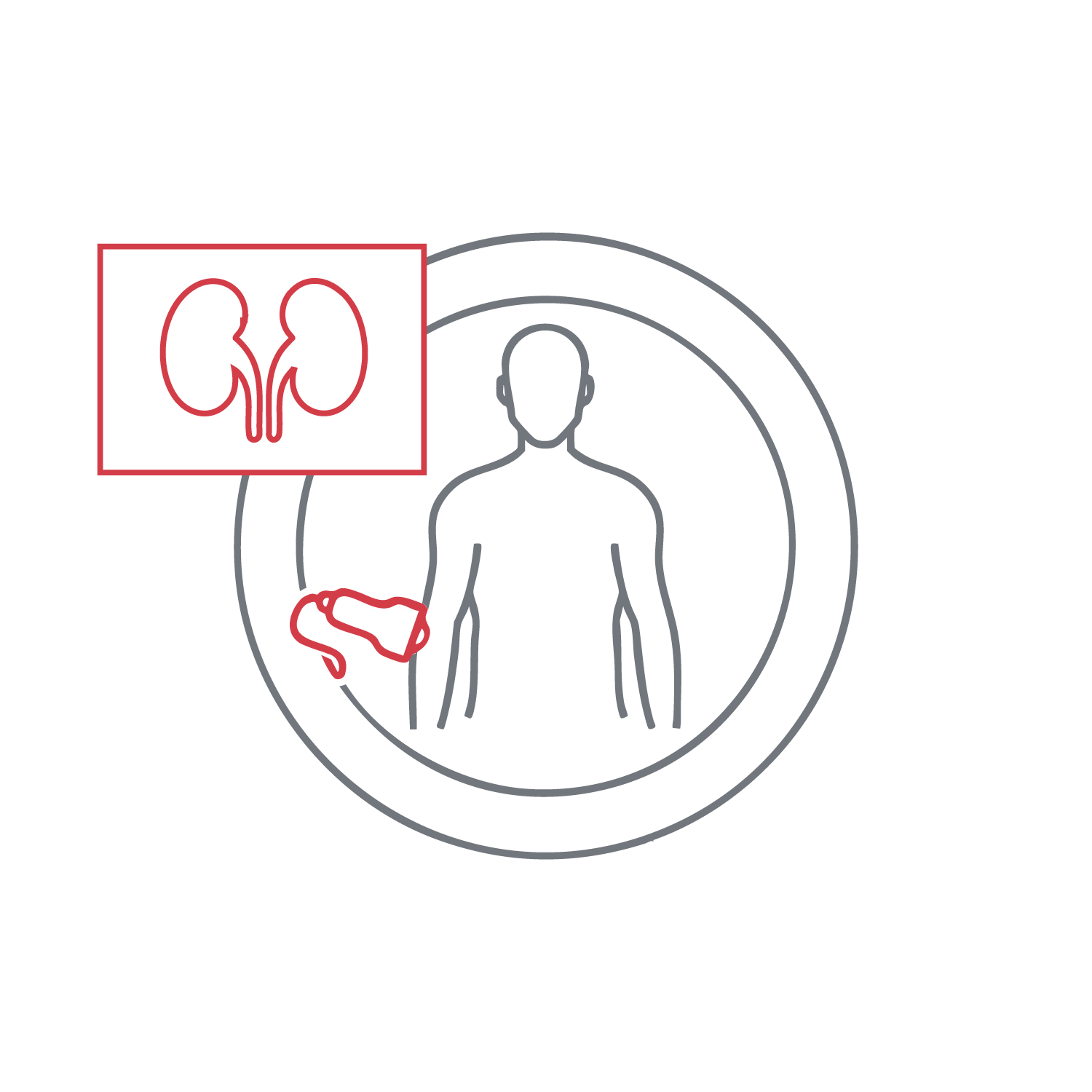

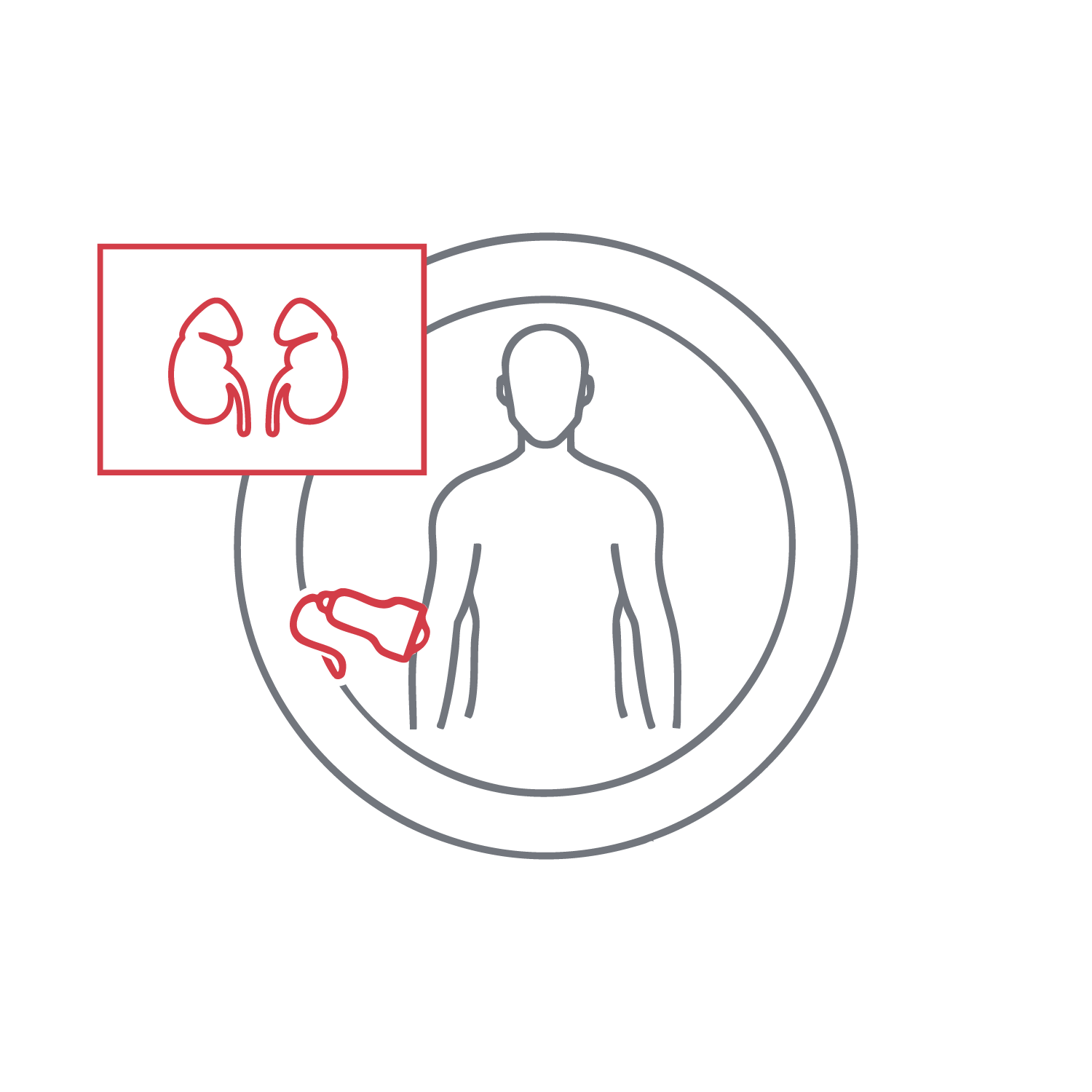
Evaluates kidney size, parenchymal texture, renal pelvis structure, and identifies stones, dilatation, or focal lesions. It is effective in detecting hydronephrosis, tumors, and infections early. Frequently used for flank pain and abnormal kidney function, it does not require contrast injection and is suitable for both diagnosis and monitoring.

Assesses the adrenal glands for abnormal size or masses, especially in cases of suspected tumors or endocrine disorders. This advanced exam requires skill for optimal visualization. It is often combined with lab tests or additional imaging and is especially useful in cases of unexplained hypertension or hormonal abnormalities.

Evaluates spleen size, structure, and potential pathological changes such as enlargement, focal lesions, or trauma. It is a key part of the diagnostic workup for unexplained fevers, hematologic conditions, or myeloproliferative disorders. The scan is quick, comfortable, and requires no preparation.

Assesses blood flow in the liver’s major vessels, including the portal vein, hepatic artery, and hepatic veins. It is crucial for evaluating portal hypertension, thrombosis, and altered flow in cirrhosis or liver tumors. Color and spectral Doppler are used to analyze direction, speed, and flow characteristics. This test is essential for monitoring chronic liver disease, liver transplants, or malignant conditions.
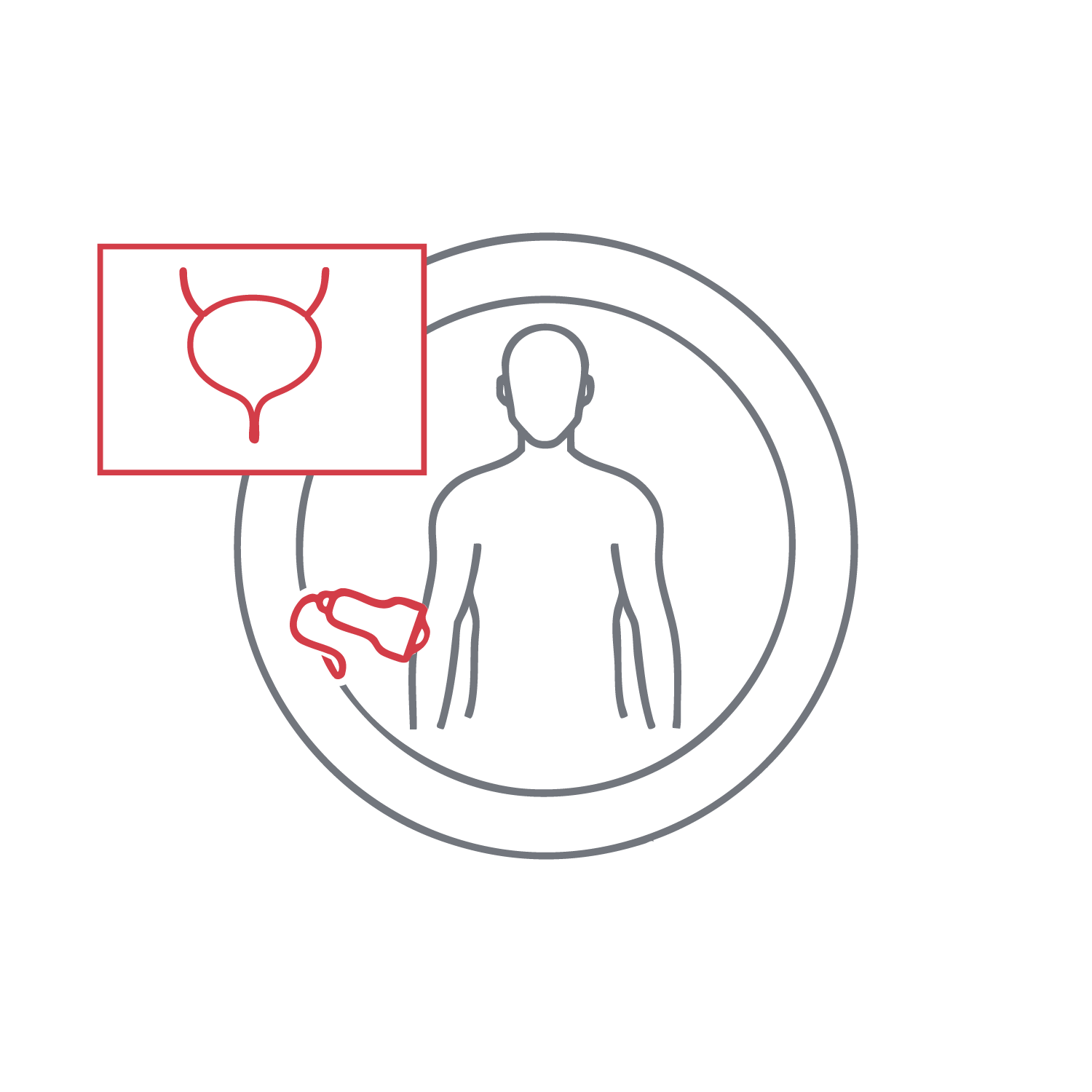

Visualizes the bladder wall, volume, and post-void residual urine. It identifies wall thickening, masses, stones, or obstructions. It is commonly used in cases of urinary dysfunction or recurrent infections. The exam is noninvasive, painless, and lasts just a few minutes. It is often performed alongside kidney and prostate imaging for a full clinical picture.
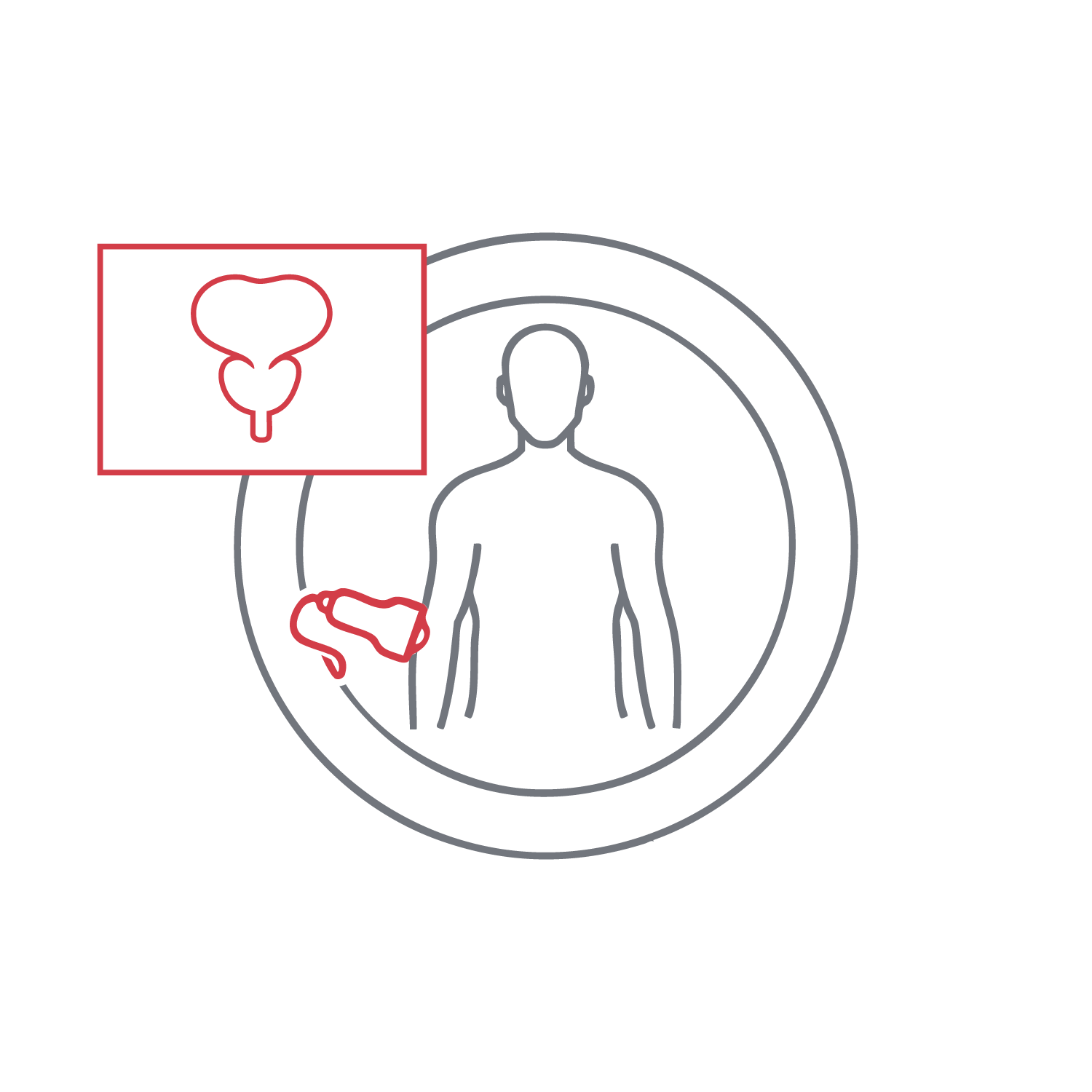
Evaluates prostate size, texture, and presence of suspicious findings. This non-invasive exam measures gland volume and checks for urinary obstruction. Especially common in men over 50, it is performed transabdominally, often requiring a full bladder. The findings assist in medication planning or further urologic workup.
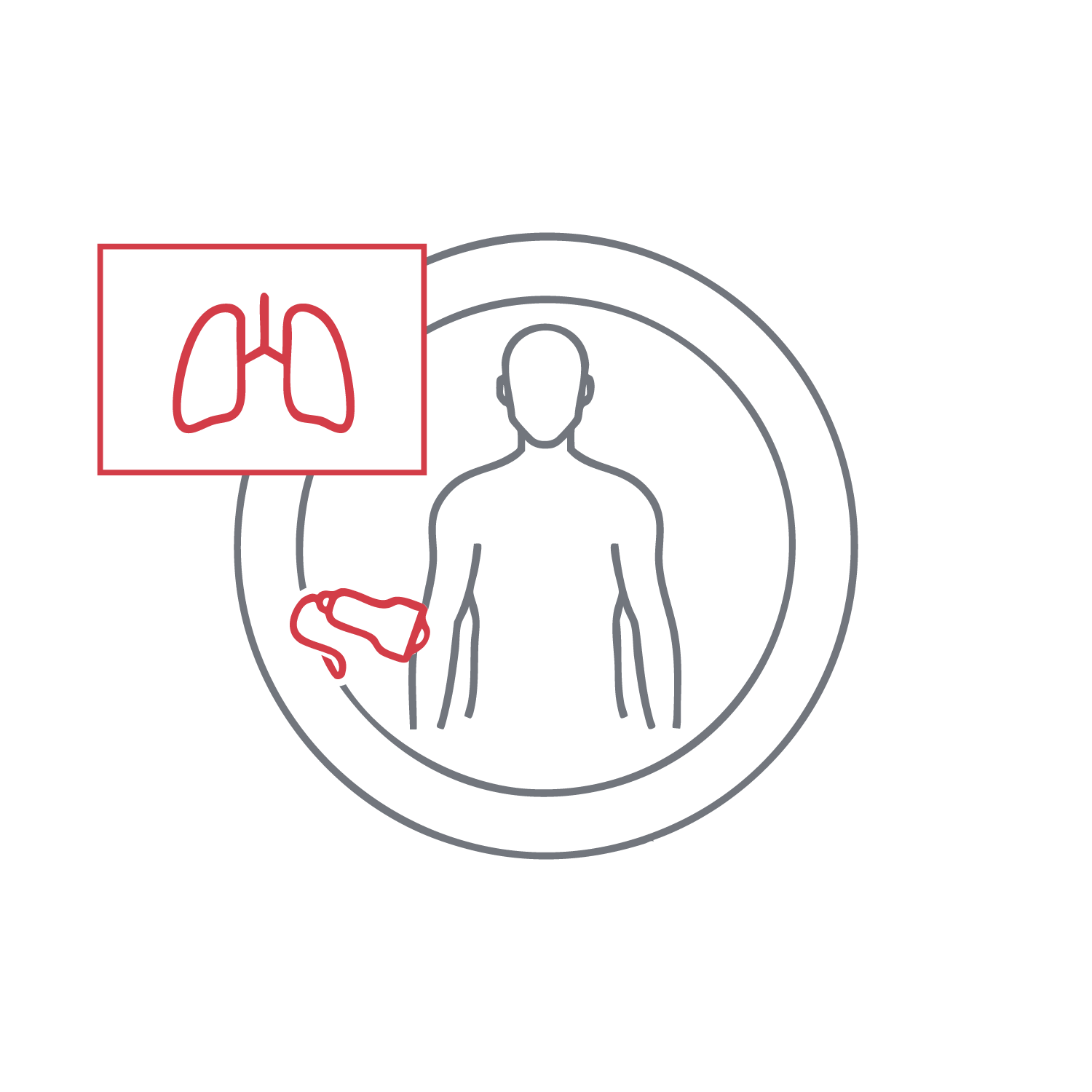

Identify and characterize pleural effusions, often seen in pneumonia, empyema, or pulmonary edema. Determine fluid volume, location, and whether it is free or loculated. It also guides therapeutic drainage. This exam is crucial for patients with respiratory symptoms or suspected lung fluid buildup.

Provides high-resolution imaging of the thyroid gland’s structure, size, borders, and abnormalities such as nodules, calcifications, or inflammation. It distinguishes between solid and cystic findings and evaluates lymph nodes when necessary. Non-invasive, radiation-free, and requiring no preparation, this exam is key in early pathology detection and further diagnostic planning. In patients with a history of thyroid cancer, ultrasound is of paramount importance for surgery planning, as well as follow-up.

Evaluates large salivary glands for stones, inflammation, ductal dilation, or tumors. This sensitive and convenient test can detect reactive or infiltrative processes and guide biopsy if needed. It is useful for lower neck swellings or jaw pain and is performed externally, without discomfort.

Detects enlarged lymph nodes and assesses their size, internal structure, vascular flow, and surrounding tissue. This scan is crucial in evaluating infectious, reactive, or malignant conditions. It often includes recommendations for biopsy or follow-up based on radiologic classification. This scan can be performed on the neck, axillae, groin, or other regions.
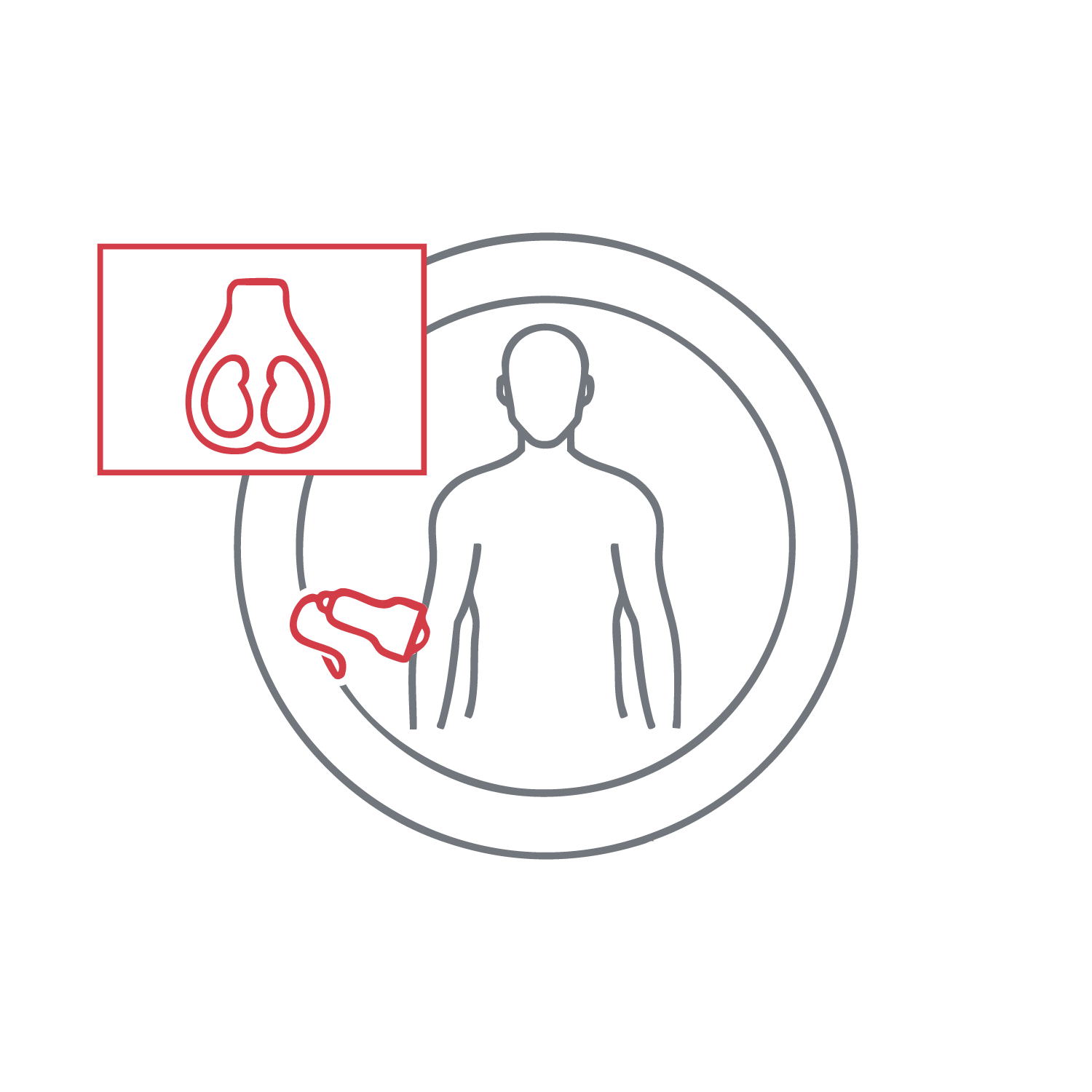

Assesses testicular anatomy, blood flow, and structures of the scrotum and epididymis. Identifies tumors, torsion, inflammation, or cysts. This highly sensitive test directly informs urgent treatment decisions. It is performed with discretion and care, prioritizing patient comfort and diagnostic accuracy.
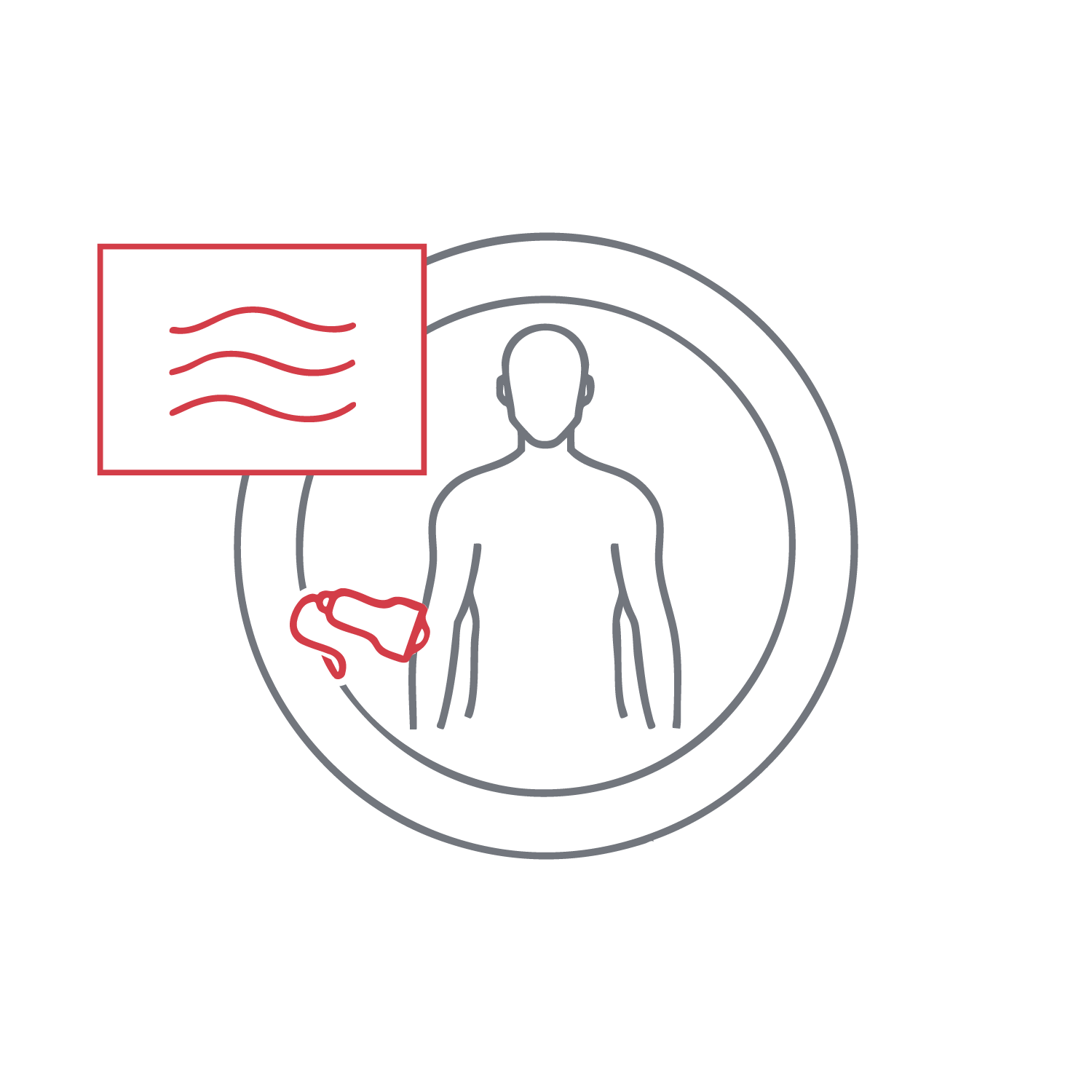

Visualizes superficial structures such as subcutaneous masses, cysts, abscesses, or inflammation. It helps differentiate tumors, infections, and trauma-related findings. The test evaluates lesion margins, texture, and relationships to adjacent structures. It is accessible, non-invasive, and radiation-free, supporting conservative or surgical management decisions.

Detects deep vein thrombosis (DVT) or chronic venous insufficiency. Evaluates blood flow, valve function, and partial or complete venous obstruction. It is essential for diagnosing leg swelling, pain, or suspected pulmonary embolism. Performed with gentle compression in a supine position to assess venous response and guide anticoagulant or surgical therapy.
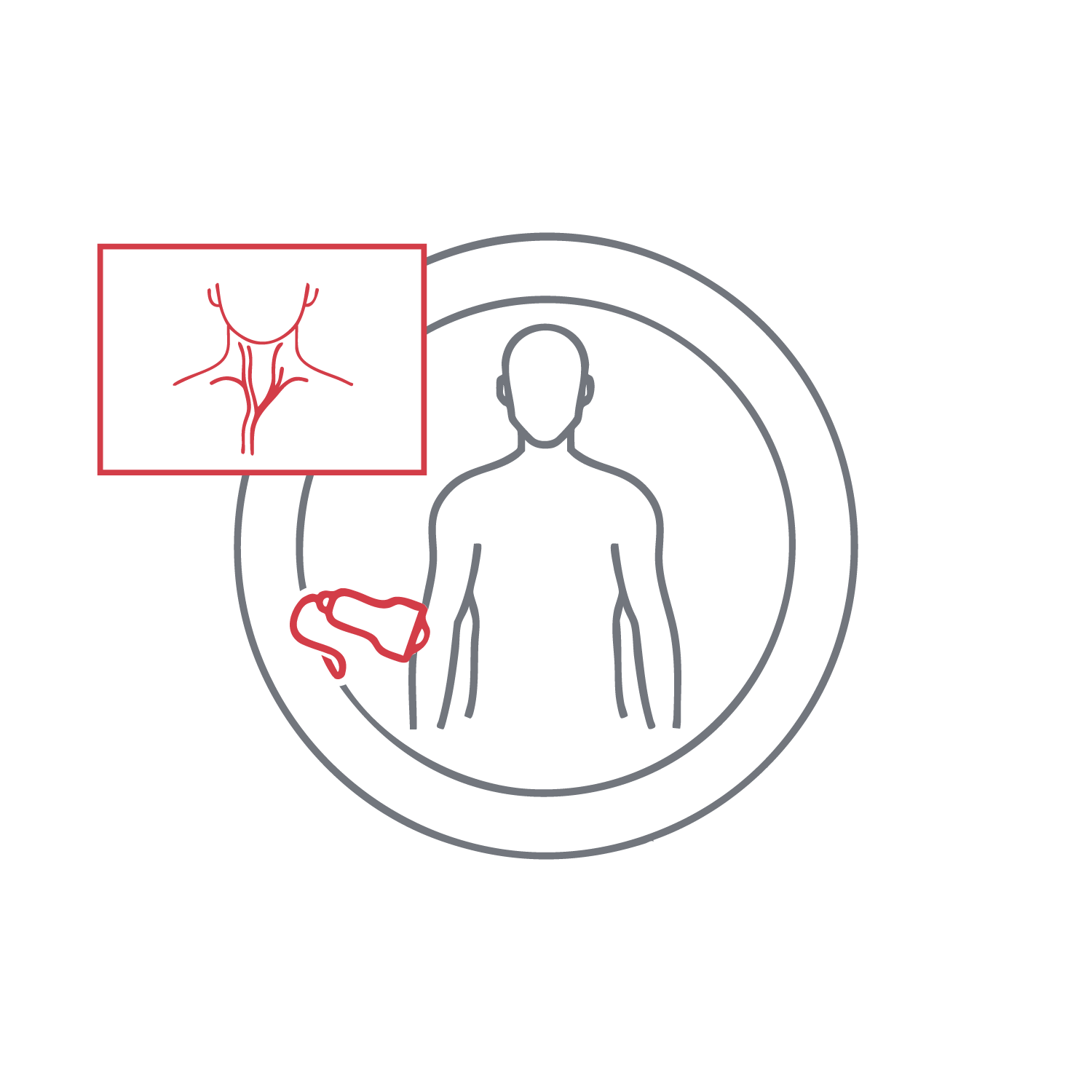

Measures blood flow in the carotid arteries, detecting narrowing or blockages that may lead to stroke. The exam quantifies stenosis and identifies atherosclerotic plaques or vessel wall irregularities. It is non-invasive, accurate, and highly predictive, especially for patients with cardiovascular risk factors or prior strokes. Results inform preventive treatment strategies.
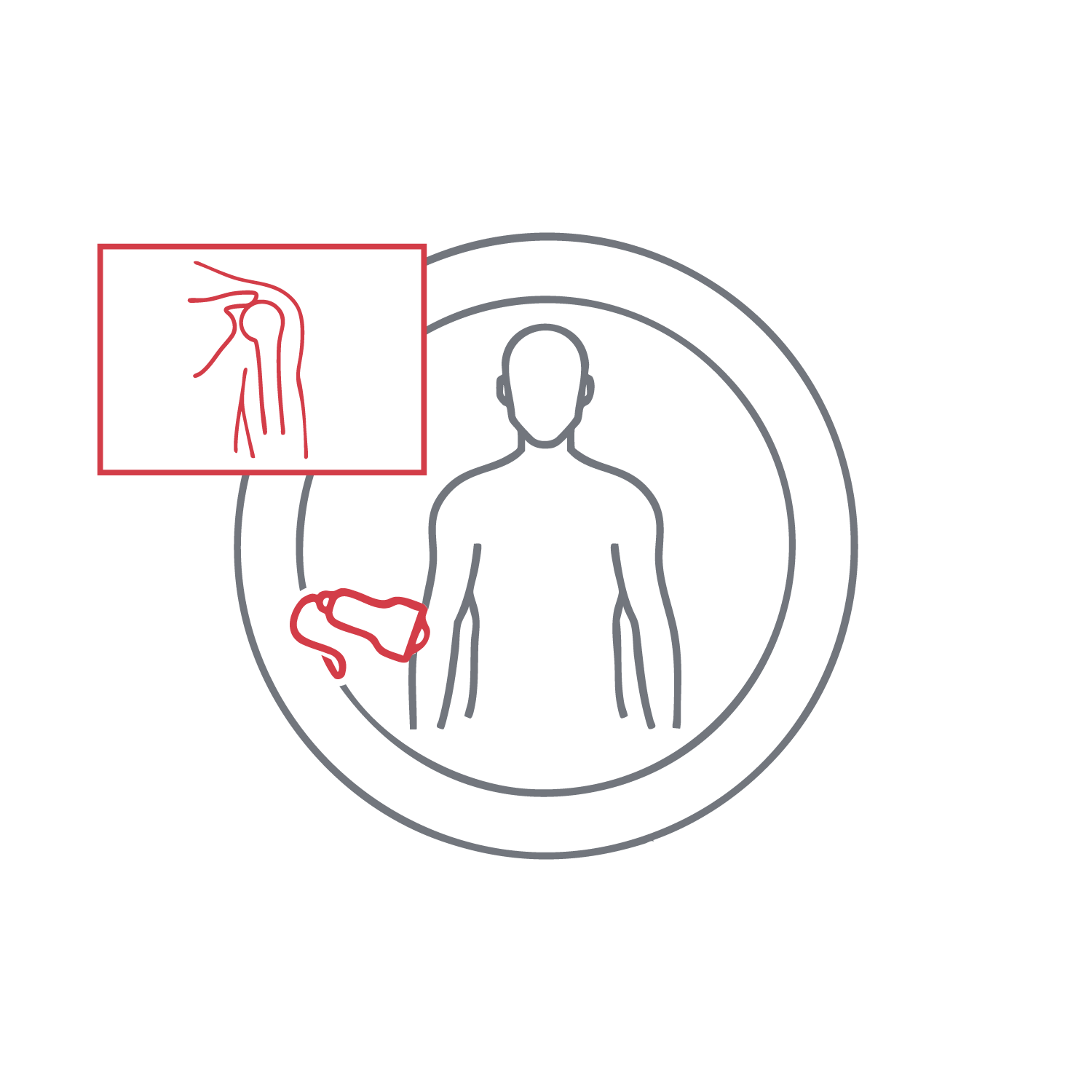

Identifies a wide range of musculoskeletal conditions and injuries. The exam targets the relevant area—shoulders, knees, hips, ankles, elbows, wrists, hands, Achilles tendon, or nerves. In some cases, it surpasses MRI in detecting intricate structures like nerves. It is also dynamic, allowing positional changes during scanning to visualize anatomy and pathology better.